
LifeCare Chiropractic Centre
08/02/2024

In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become a common concern affecting both mental and physical well-being. At LifeCare Chiropractic Centre, we recognize the intricate relationship between stress, mental health, and spinal health. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the impact of stress on mental and spinal health, gentle exercises and stretches to alleviate stress, and how chiropractic treatments can effectively manage stress-related symptoms while promoting overall well-being.
Understanding Stress

Definition and Types of Stress
Stress is the body’s physiological response to external or internal demands, categorized into acute and chronic stress.
Acute stress is a short-term response to specific events, activating the body’s “fight or flight” mechanism with increased heart rate and alertness. It’s triggered by situations like deadlines or public speaking and subsides once the stressor is resolved, returning the body to baseline.
Chronic stress is prolonged exposure to stressors, leading to sustained physiological and psychological strain. It arises from factors like work pressures or chronic illness and disrupts the stress response system. This leads to health issues such as cardiovascular disease and mental health disorders. Managing chronic stress requires proactive strategies like stress management techniques and therapy to address underlying stressors effectively.

Physiological Response
When we feel stressed, our body reacts in a specific way to help us cope. It releases chemicals like adrenaline and cortisol, which make our heart beat faster, increase blood pressure, and help us breathe more quickly. These chemicals give us extra energy and make us more alert. Our body also activates the “fight or flight” response, which is like a built-in alarm system. It prepares us to face the stressful situation or run away from it. This response helps us deal with the stress at that moment. Once the stress is over, our body goes back to its normal state. This reaction is important because it helps us handle challenges and keep ourselves safe when we feel stressed.

Impact on Mental Health
Stress has a significant impact on our mental health by affecting our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. When we experience stress, our minds may become preoccupied with worries and concerns, making it challenging to focus or concentrate on tasks. Persistent stress can lead to feelings of anxiety, which may manifest as constant worrying, restlessness, or panic attacks. Additionally, stress can contribute to feelings of sadness or hopelessness, potentially leading to depression. Our sleep patterns may also be disrupted by stress, resulting in difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night. Furthermore, stress can influence our behavior, causing irritability, mood swings, or changes in appetite. These mental health effects of stress highlight the importance of practicing self-care and seeking support to manage stress effectively and maintain overall well-being.

Behavioral and Emotional Effects
Stress can have a range of behavioral and emotional effects, impacting how we think, feel, and act. Behaviorally, stress may lead to changes in our habits and actions. For example, we might withdraw from social activities, experience difficulty concentrating, or have trouble making decisions. We may also engage in unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as overeating, smoking, or excessive use of alcohol or drugs, as a way to manage stress.
Emotionally, stress can cause a variety of responses. We may feel overwhelmed, anxious, or tense, experiencing a constant state of worry or nervousness. This can lead to irritability, mood swings, or outbursts of anger. Additionally, stress can contribute to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or despair, which may indicate symptoms of depression. Some individuals may also experience feelings of guilt or inadequacy, especially if they perceive themselves as unable to cope with the demands of stressors in their lives.
The Connection Between Stress, Mental Health, and Spinal Health:

Stress and Spinal Health
Chronic stress often leads to muscle tension, particularly in the neck, shoulders, and upper back regions. Prolonged muscle tension can result in spinal misalignments, known as subluxations, which interfere with proper nerve function and contribute to a range of spinal health issues.

Mental Health and Spinal Health
Research indicates a bidirectional relationship between mental health and spinal health. Mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression are associated with increased muscle tension and spinal misalignments, while spinal misalignments can exacerbate stress-related symptoms and hinder the body’s ability to cope with stress.
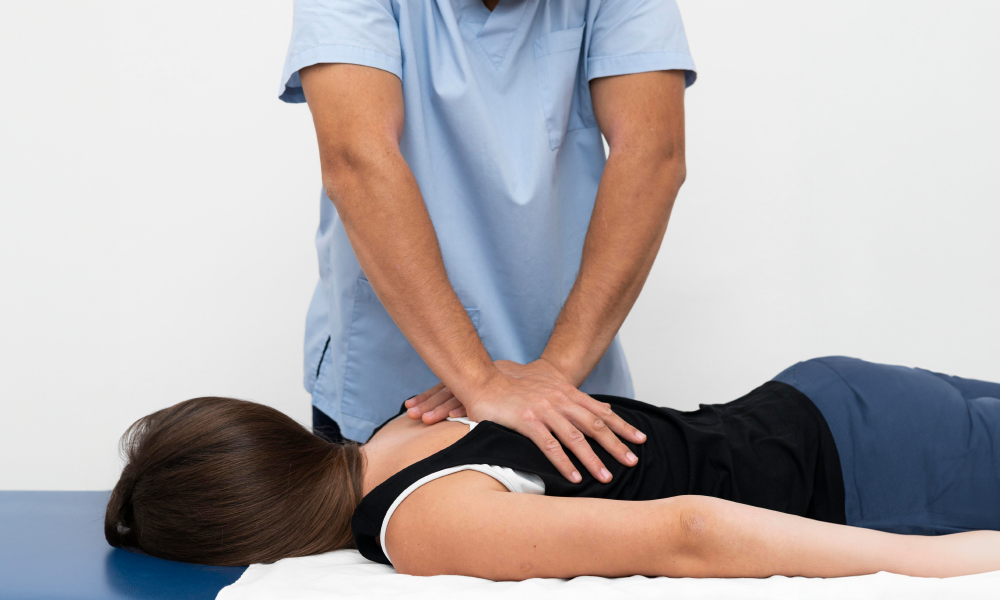
The Role of Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic treatments focus on addressing spinal misalignments through manual adjustments, thereby restoring proper alignment and function to the spine. By correcting subluxations and reducing nerve interference, chiropractic care can alleviate muscle tension, improve nerve communication, and promote overall spinal health.
Gentle Exercises and Stretches for Stress Relief and Spinal Health:

Deep Breathing Techniques:
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, involves inhaling deeply through the nose, allowing the abdomen to expand fully, and exhaling slowly through the mouth. Deep breathing exercises promote relaxation, reduce stress hormones, and enhance the oxygenation of tissues.

Neck and Shoulder Stretches:
Gentle neck stretches, such as side-to-side neck tilts and chin tucks, help alleviate tension in the neck and shoulder muscles. Shoulder rolls and shoulder blade squeezes can also relieve stiffness and promote flexibility in the upper body.

Spinal Mobility Exercises:
Cat-Cow stretches, spinal twists, and pelvic tilts are effective exercises for improving spinal mobility and relieving tension in the back. These exercises target the muscles surrounding the spine, promoting flexibility and reducing the risk of spinal misalignments.
Incorporate these simple exercises into your daily routine to combat the effects of stress. Remember to listen to your body and avoid any movements that cause pain. These exercises are designed to be discreet and effective, helping you maintain better posture and feel more energized throughout your day.
Aligning Wellness with LifeCare Chiropractic Centre
At LifeCare Chiropractic Centre, we provide comprehensive and personalised chiropractic treatment plans to improve your quality of life and have a stress free body.

Integrated & Personalised Care

Experienced Professional Chiropractor

Non-Invasive & Lasting Results

Get In Touch With Us Now!



