Life Care Diagnostic
January 13, 2021
Lung infections happen when pathogens collect in a person’s air sacs and begin to grow. The air sacs may become filled with pus and fluid, which can make breathing more difficult, cause chest pain, and lead to a cough.
The primary types of lung infection include pneumonia, bronchitis and bronchiolitis. These conditions are typically caused by bacteria and viruses. It’s much rarer for a lung infection to be caused by fungi. Fungal infections are generally more common in people who have weakened immune systems.


The following signs and symptoms of lung infection should alert you to contact your doctor right away.

A collection of infected fluid (pus) in the space between the lung and the surrounding membrane (pleural space), an empyema can build up and put pressure on the lungs.
An excess of fluid in the pleural space that can make it hard for the lungs to fully expand and breathe deeply.
A lung abscess is a rare but serious complication that forms when the body’s immune system attempts to wall off the infection.
An untreated abscess could result in the onset of sepsis, a dangerous overactive and toxic immune response.
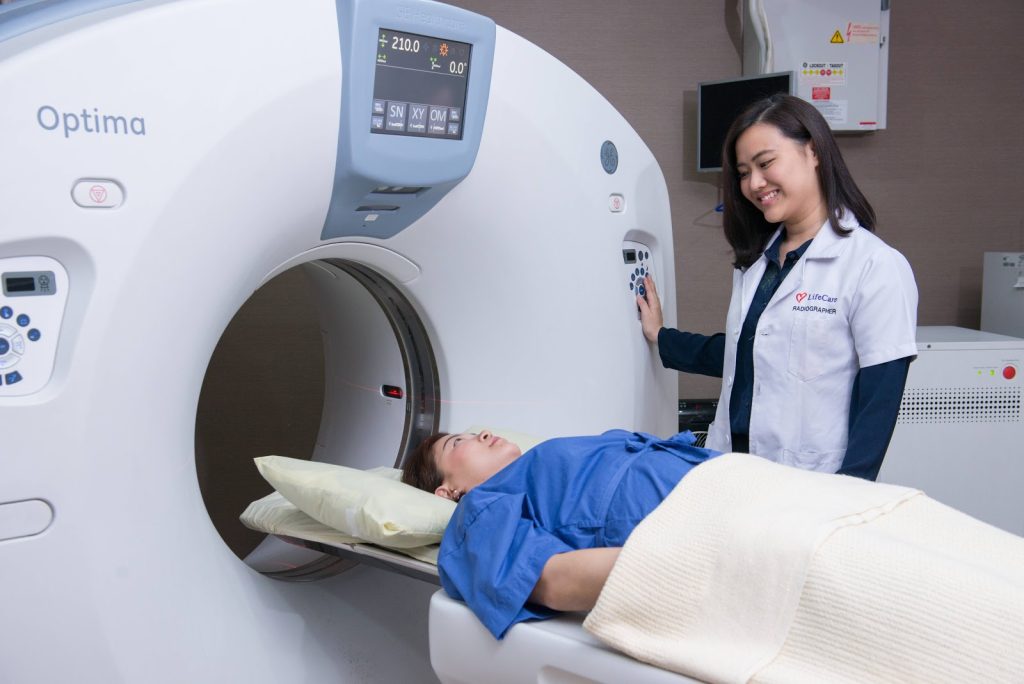
A combination of imaging studies, including chest X-ray and computed tomography (CT scan) may be used to diagnose lung infections. In addition, a sputum examination and blood tests may be required to determine the type of infection.
When to See A Doctor
Lung infections can get worse if left untreated. If you’ve noticed a change in mucus, cough or wheezing that seems worse than usual, see your doctor at once.
As preventive care, you may want to get protected with Viral and Bacteria Lung Infection Vaccinations – Fluarix Tetra + Pneumovax 23. Add them into your existing cart before check-out to enjoy special prices.
KKLIU 1600/2021
